Django with Kubenetes I: local - Gunicorn and Nginx

In this article, before containerizing a Django app, we just setting up Django with Gunicorn and Nginx. We'll use Docker in the next article.
The code is available from Django-Gunicorn-Nginx-Docker-Kubernetes .
Terminology (Django):
Nginx: listens on port 80 for incoming HTTP requests from the internet.
Gunicorn: listens on another port(8000 is the popular one) for HTTP requests from Nginx. Gunicorn is configured with our Django web app. It serves dynamic contents passed from Nginx. (Note that Gunicorn can handle static(css/js/images) but Nginx is better optimized for it. So, we need both Nginx and Gunicorn for a proper Django deployment.
WSGI (Web Server Gateway Interface) servers (such as Gunicorn, uWSGI, or mod_wsgi). A web server faces the outside world. It can serve files (HTML, images, CSS, etc) directly from the file system. However, it can't talk directly to Django applications; it needs something that will run the application, feed it requests from web clients (such as browsers) and return responses.
With Nginx, mod_wsgi is out of the picture, and we have to choose between Gunicorn and uWSGI : WSGI sits between Nginx(web server) and django (python app). The WSGI server doesn't talk to our Django project, it imports our Django project. It does something like this:
from mysite.wsgi import application application(args)
uWSGI: It is a WSGI (python standard) implementation. The uWSGI is a fully-featured application server. Generally, uWSGI is paired with a reverse proxy (such as Nginx). It creates a Unix socket, and serves responses to the web server via the uWSGI protocol.
the web client <-> the web server <-> the socket <-> uwsgi <-> Django
But we're not going to use uWSIG in this tutorial.
myproject/mysite:
myproject/ manage.py mysite/ __init__.py settings.py urls.py wsgi.py
We can collect all of the static content into ~/mysite/(assets or static) specified as STATIC_ROOT in settings.py. For example, like this:
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(PROJECT_ROOT, 'assets')
The command is:
(venv)$ ./manage.py collectstatic
There are several commands which we will use to interact with migrations and Django's handling of database schema:
- migrate: it is responsible for applying and applying migrations.
- makemigrations: it is responsible for creating new migrations based on the changes we have made to our models.
$ ./manage.py makemigrations $ ./manage.py migrate
$ python manage.py createsuperuser
Gunicorn is a pure-Python WSGI HTTP server and it has no dependencies and is easy to install and use.
As a Python HTTP server, Gunicorn interfaces with both Nginx and our actual python web-app code to serve dynamic content while Nginx is responsible for serving static content and others.
We can test Gunicorn by typing:
(venv)$ gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 mysite.wsgi:application
The mysite.wsgi:application is an accurate path to the WSGI callable. This means that when we're in the project directory, we should be able to reach the callable named application by looking in the mysite.wsgi module which translates to a file called ./mysite/wsgi.py.
Or simpler command:
(venv)$ gunicorn mysite.wsgi
This will start one process running one thread listening on 127.0.0.1:8000. It requires that our project be on the Python path; the simplest way to ensure that is to run this command from the same directory as our manage.py file.
The Gunicorn WSGI server was configured to use the object defined in einstinish/wsgi.py file by WSGI_APPLICATION setting.
from django.core.wsgi import get_wsgi_application application = get_wsgi_application()
Now, our web server (e.g., Nginx, Apache) can communicate with a django-uwsgi worker process to serve dynamic content.
Actually, Gunicorn receives the request from Nginx, translates it to a Web Server Gateway Interface compatible request and calls the Django's request handler method.
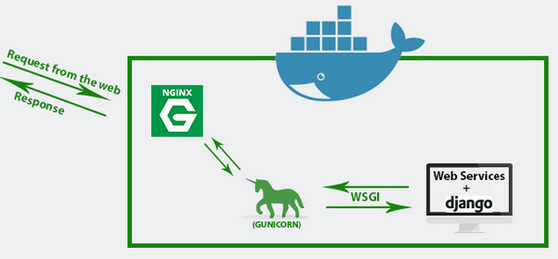
The /etc/nginx/sites-available/mysite.conf looks like this:
server {
# the port your site will be served on
listen 80;
# the domain name it will serve for
# server_name .domain.tld ip.adress; # substitute by your FQDN and machine's IP address
server_name localhost 127.0.0.1; # substitute by your FQDN and machine's IP address
charset utf-8;
#Max upload size
client_max_body_size 75M; # adjust to taste
# Django media
location /media {
alias /var/www/path/to/your/project/media; # your Django project's media files
}
location /assets {
alias /var/www/path/to/your/project/static; # your Django project's static files
}
# Finally, send all non-media requests to the Django server.
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
We'll get the app from port 80 while Gunicorn is using port 8000!
Setup softlink (in my case, the site name is einsteinish):
$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/einsteinish.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/einsteinish.conf
Then, run the Gunicorn and Nginx:
$ gunicorn einsteinish.wsgi $ sudo systemctl restart nginx
This is local, so let's add the host in /etc/hosts:
127.0.0.1 einstein.com
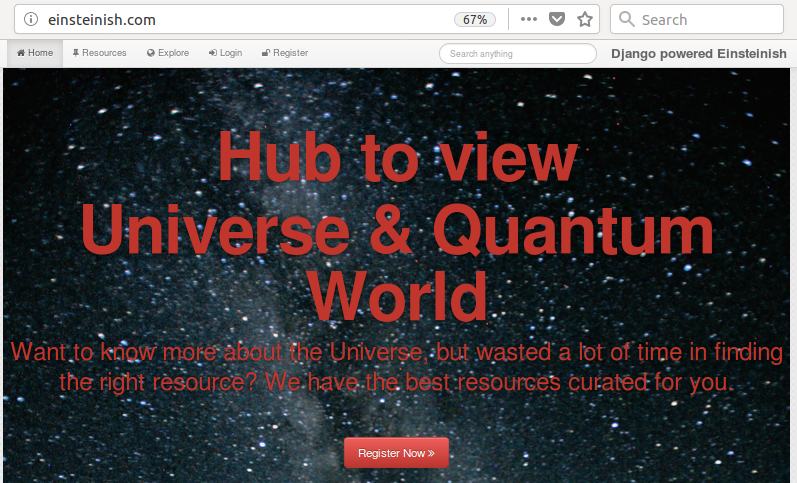
Now, we can see our app:
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization