Django with Kubenetes II: Gunicorn and Nginx with Docker Compose

In this article, we'll deploy Django app (bare minimum) using Docker-compose. The other pieces are Nginx and Gunicorn.
Here are the files after everything's done.
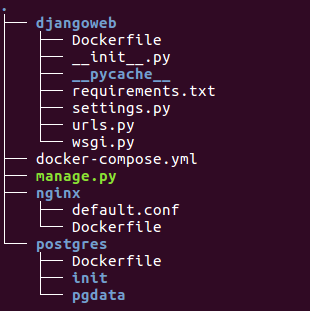
Note that we created a Dockerfile in each of the service (web, nginx, and postgres). As we already know, the Dockerfile defines an application's image content via one or more build commands that configure that image. Once built, we can run the image in a container.
The result should look like this:
The requirements.txt in djangoweb directory is used by the RUN pip install -r requirements.txt command in the Dockerfile:
FROM python:3.6 ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1 RUN mkdir /code WORKDIR /code ADD requirements.txt /code/ RUN pip install -r requirements.txt ADD . /code/
This Dockerfile starts with a Python 3 parent image. The parent image is modified by adding a new code directory. The parent image is further modified by installing the Python requirements defined in the requirements.txt file.
The docker-compose.yml file describes the services that make our app.
"Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container Docker applications. With Compose, you use a YAML file to configure your application's services. Then, with a single command, you create and start all the services from your configuration." - Overview of Docker Compose
With the following docker-compose.yml file, we create the database service named db using the PostgreSQL alpine Linux, create the nginx service using the Nginx alpine Linux, and create our Django container service named web using the custom docker images generated from our Dockerfile.
docker-compose.yml:
version: '3'
services:
db:
#image: postgres
build: ./postgres
restart: unless-stopped
expose:
- "5432"
environment: # will be used by the init script
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
POSTGRES_DB: postgres
volumes:
- ./postgres/pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data/ # persist container's db data to local pgdata/ (mounted)
web:
build: ./djangoweb
# command: python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000
command: gunicorn djangoweb.wsgi -b 0.0.0.0:8000
volumes:
- .:/code
expose:
- "8000"
depends_on:
- db
nginx:
restart: always
build: ./nginx/
ports:
- "8087:80" # host:container
links:
- web
The compose file also describes which Docker images these services use, how they link together (depends_on), any volumes they might need mounted inside the containers.
The expose exposes ports without publishing them to the host machine - they'll only be accessible to linked services. Only the internal port can be specified.
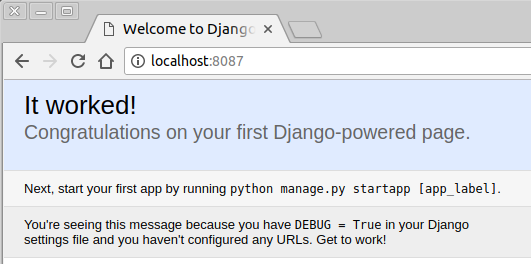
As shown earlier, we get our app via http://localhost:8087.
Note also that we mounted volumes relative to the Compose file:
- For postgres service:
volumes: - ./postgres/pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data/
- For web:
volumes: - .:/code
We are using restart:
no is the default restart policy, and it does not restart a container under any circumstance. When always is specified, the container always restarts. The on-failure policy restarts a container if the exit code indicates an on-failure error.restart: "no" restart: always restart: on-failure restart: unless-stopped
Ref: Docker Guide: Dockerizing Python Django Application
We will install docker-ce community edition and docker-compose that support compose file version 3.
$ sudo apt install -y docker-ce $ docker --version Docker version 18.06.1-ce, build e68fc7a
Then, we may want to add a new user named 'kube' and add it to the docker group:
$ sudo useradd -m -d /home/kube -s /bin/bash kube $ sudo usermod -a -G docker kube $ sudo passwd kube
Login as the "kube" user and run docker command as below and make sure we get the hello-world message from Docker:
$ su - kube $ docker run hello-world ... Hello from Docker!
we will be using the latest docker-compose support for compose file version 3 and download the latest version of docker-compose using curl command to the '/usr/local/bin' directory and make it executable using chmod:
$ sudo curl -L https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.21.0/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m) -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose $ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose $ docker-compose version docker-compose version 1.21.0, build 5920eb0 docker-py version: 3.2.1 CPython version: 3.6.5 OpenSSL version: OpenSSL 1.0.1t 3 May 2016
Now, let's build the docker images using the docker-compose command.
If we change a service's Dockerfile or the contents of its build directory, we can run docker-compose build to rebuild it.
$ docker-compose build Building db Step 1/2 : FROM postgres:10.3-alpine ... Step 2/2 : COPY ./init/db_setup.sh /docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/db-setup.sh ... Successfully tagged django-gunicorn-nginx-2_db:latest Building web Step 1/7 : FROM python:3.6 ... Step 2/7 : ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1 ... Step 3/7 : RUN mkdir /code ... Step 4/7 : WORKDIR /code ... Step 5/7 : ADD requirements.txt /code/ ... Step 6/7 : RUN pip install -r requirements.txt ... Installing collected packages: pytz, Django, psycopg2-binary, gunicorn Successfully installed Django-1.11.15 gunicorn-19.7.0 psycopg2-binary-2.7.5 pytz-2018.5 ... Step 7/7 : ADD . /code/ ... Successfully tagged django-gunicorn-nginx-2_web:latest Building nginx Step 1/2 : FROM nginx ... Step 2/2 : COPY default.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf ... Successfully tagged django-gunicorn-nginx-2_nginx:latest
Start all services:
$ docker-compose up Creating network "django-gunicorn-nginx-2_default" with the default driver Creating django-gunicorn-nginx-2_db_1 ... done Creating django-gunicorn-nginx-2_web_1 ... done Creating django-gunicorn-nginx-2_nginx_1 ... done Attaching to django-gunicorn-nginx-2_db_1, django-gunicorn-nginx-2_web_1, django-gunicorn-nginx-2_nginx_1 db_1 | 2018-09-30 17:24:54.489 UTC [1] LOG: listening on IPv4 address "0.0.0.0", port 5432 db_1 | 2018-09-30 17:24:54.489 UTC [1] LOG: listening on IPv6 address "::", port 5432 db_1 | 2018-09-30 17:24:54.845 UTC [1] LOG: listening on Unix socket "/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432" db_1 | 2018-09-30 17:24:55.316 UTC [18] LOG: database system was shut down at 2018-09-30 01:12:15 UTC db_1 | 2018-09-30 17:24:55.463 UTC [1] LOG: database system is ready to accept connections web_1 | [2018-09-30 17:24:59 +0000] [1] [INFO] Starting gunicorn 19.7.0 web_1 | [2018-09-30 17:24:59 +0000] [1] [INFO] Listening at: http://0.0.0.0:8000 (1) web_1 | [2018-09-30 17:24:59 +0000] [1] [INFO] Using worker: sync web_1 | [2018-09-30 17:24:59 +0000] [8] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 8 nginx_1 | 192.168.80.1 - - [30/Sep/2018:17:25:09 +0000] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 1716 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:62.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/62.0" "-"
The docker-compose up command aggregates the output of each container (essentially running docker-compose logs -f). When the command exits, all containers are stopped. Running docker-compose up -d starts the containers in the background and leaves them running.
Wait for Docker to build our Python image and download the nginx and postgresql docker images. Once it's complete, check running container and list docker images on the system using following commands.
Then, we will get three containers running and list of Docker images on the system as shown below:
$ docker-compose ps
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c8d37a368e06 djangoproject-2_nginx "nginx -g 'daemon of…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:8087->80/tcp djangoproject-2_nginx_1
11a72245216a djangoproject-2_web "gunicorn djangoweb.…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 8000/tcp djangoproject-2_web_1
5bd3e0ad7ec3 djangoproject-2_db "docker-entrypoint.s…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 5432/tcp djangoproject-2_db_1
$ docker-compose images
Container Repository Tag Image Id Size
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
djangoproject-2_db_1 djangoproject-2_db latest 7b1990e7f317 37.7 MB
djangoproject-2_nginx_1 djangoproject-2_nginx latest 6e84cc2ff709 104 MB
djangoproject-2_web_1 djangoproject-2_web latest 1cbc8e6d2726 921 MB
As we can see nginx container has it's 80 mapped to port 8087 of the docker host (machine on which we're running docker-compose). Simply hit the localhost i.e. http://localhost:8087 and we'll have the Django homepage appear, and we should see the following:

To stop a docker application that is running in the background, use the docker-compose stop. There are two steps to stop a docker application containers:
- First, stop the running containers using docker-compose stop
- Second, remove the stopped containers using docker-compose rm -f
$ docker-compose stop && docker-compose rm -f
Here, we used && which will execute the 2nd command only after the 1st command is successful. So, it will do "rm -f", only after stopping the docker containers successfully.
We can also use docker-compose down to stop containers and remove containers, networks, volumes, and images created by up.
By default, the only things removed are:
- Containers for services defined in the Compose file
- Networks defined in the networks section of the Compose file
- The default network, if one is used
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization