Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization
In this chapter, we'll install a single-node Hadoop cluster backed by the Hadoop Distributed File System on Ubuntu.
Hadoop framework is written in Java!!
# Update the source list $ sudo apt-get update # The OpenJDK project is the default version of Java # that is provided from a supported Ubuntu repository. $ sudo apt-get install default-jdk $ java -version java version "1.7.0_55" OpenJDK Runtime Environment (IcedTea 2.4.7) (7u55-2.4.7-1ubuntu1) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.51-b03, mixed mode)
k@k:~$ sudo addgroup hadoop Adding group `hadoop' (GID 1002) ... Done. k@k:~$ sudo adduser --ingroup hadoop hduser Adding user `hduser' ... Adding new user `hduser' (1002) with group `hadoop' ... Creating home directory `/home/hduser' ... Copying files from `/etc/skel' ... Enter new UNIX password: Retype new UNIX password: passwd: password updated successfully Changing the user information for hduser Enter the new value, or press ENTER for the default Full Name []: Room Number []: Work Phone []: Home Phone []: Other []: Is the information correct? [Y/n] Y
ssh has 2 main components :
- ssh : The command we use to connect to remote machines - the client.
- sshd : The daemon that is running on the server and allows clients to connect to the server.
The ssh is pre-enabled on Linux, but in order to start sshd daemon, we need to install ssh first. Use this command to do that :
$ sudo apt-get install ssh
This will install ssh on our machine. If we get something similar to the following, we can think it is setup properly:
$ which ssh /usr/bin/ssh $ which sshd /usr/sbin/sshd
Hadoop requires SSH access to manage its nodes, i.e. remote machines plus our local machine. For our single-node setup of Hadoop, we therefore need to configure SSH access to localhost.
So, we need to have SSH up and running on our machine and configured it to allow SSH public key authentication.
Hadoop uses SSH (to access its nodes) which would normally require the user to enter a password. However, this requirement can be eliminated by creating and setting up SSH certificates using the following commands. If asked for a filename just leave it blank and press the enter key to continue.
k@k:~$ su hduser Password: hduser@k:/home/k$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -P "" Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/hduser/.ssh/id_rsa): Created directory '/home/hduser/.ssh'. Your identification has been saved in /home/hduser/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/hduser/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: 5a:48:c1:c2:18:f7:93:b5:7e:d2:b8:4b:c3:19:7b:bf hduser@k The key's randomart image is: +--[ RSA 2048]----+ | .+... . | | ..o..+ . | | .= . | | . + o | | . S o | | + B | | . B . | | . + . | | . E. | +-----------------+ hduser@k:/home/k$ cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> $HOME/.ssh/authorized_keys
The second command adds the newly created key to the list of authorized keys so that Hadoop can use ssh without prompting for a password.
We can check if ssh works:
hduser@k:/home/k$ ssh localhost The authenticity of host 'localhost (127.0.0.1)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is e1:8b:a0:a5:75:ef:f4:b4:5e:a9:ed:be:64:be:5c:2f. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added 'localhost' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Welcome to Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.13.0-27-generic x86_64) * Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/ The programs included with the Ubuntu system are free software; the exact distribution terms for each program are described in the individual files in /usr/share/doc/*/copyright. Ubuntu comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by applicable law.
$ wget http://mirrors.sonic.net/apache/hadoop/common/hadoop-2.4.1/hadoop-2.4.1.tar.gz $ tar xvzf hadoop-2.4.1.tar.gz
We want to move the Hadoop installation to the /usr/local/hadoop directory using the following command:
$ sudo mv hadoop-2.4.1 /usr/local/hadoop $ sudo chown -R hduser:hadoop hadoop $ pwd /usr/local/hadoop $ ls bin etc include lib libexec LICENSE.txt NOTICE.txt README.txt sbin share
The following files will have to be modified to complete the Hadoop setup:
- ~/.bashrc
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template
- /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
1. ~/.bashrc:
Before editing the .bashrc file in our home directory, we need to find the path where Java has been installed to set the JAVA_HOME environment variable using the following command:
$ update-alternatives --config java There is only one alternative in link group java (providing /usr/bin/java): /usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64/jre/bin/java Nothing to configure.
Now we can append the following to the end of ~/.bashrc
#HADOOP VARIABLES START export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64 export HADOOP_INSTALL=/usr/local/hadoop export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_INSTALL/bin export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_INSTALL/sbin export HADOOP_MAPRED_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL export HADOOP_COMMON_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL export HADOOP_HDFS_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL export YARN_HOME=$HADOOP_INSTALL export HADOOP_COMMON_LIB_NATIVE_DIR=$HADOOP_INSTALL/lib/native export HADOOP_OPTS="-Djava.library.path=$HADOOP_INSTALL/lib" #HADOOP VARIABLES END
2. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hadoop-env.sh
We need to set JAVA_HOME by modifying hadoop-env.sh file
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-7-openjdk-amd64
Adding the above statement in the hadoop-env.sh file ensures that the value of JAVA_HOME variable will be available to Hadoop whenever it is started up.
3. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml:
The /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml file contains configuration properties that Hadoop uses when starting up. This file can be used to override the default settings that Hadoop starts with.
$ sudo mkdir -p /app/hadoop/tmp $ sudo chown hduser:hadoop /app/hadoop/tmp
Open the file and enter the following in between the <configuration></configuration> tag:
<configuration> <property> <name>hadoop.tmp.dir</name> <value>/app/hadoop/tmp</value> <description>A base for other temporary directories.</description> </property> <property> <name>fs.default.name</name> <value>hdfs://localhost:54310</value> <description>The name of the default file system. A URI whose scheme and authority determine the FileSystem implementation. The uri's scheme determines the config property (fs.SCHEME.impl) naming the FileSystem implementation class. The uri's authority is used to determine the host, port, etc. for a filesystem.</description> </property> </configuration>
4. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
By default, the /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/ folder contains the /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template file which has to be renamed/copied with the name mapred-site.xml:
$ cp /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml.template /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/mapred-site.xml
The mapred-site.xml file is used to specify which framework is being used for MapReduce. We need to enter the following content in between the <configuration></configuration> tag:
<configuration> <property> <name>mapred.job.tracker</name> <value>localhost:54311</value> <description>The host and port that the MapReduce job tracker runs at. If "local", then jobs are run in-process as a single map and reduce task. </description> </property> </configuration>
5. /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml
The /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml file needs to be configured for each host in the cluster that is being used. It is used to specify the directories which will be used as the namenode and the datanode on that host.
Before editing this file, we need to create two directories which will contain the namenode and the datanode for this Hadoop installation. This can be done using the following commands:
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode $ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/datanode $ sudo chown -R hduser:hadoop /usr/local/hadoop_store
Open the file and enter the following content in between the <configuration></configuration> tag:
<configuration> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> <description>Default block replication. The actual number of replications can be specified when the file is created. The default is used if replication is not specified in create time. </description> </property> <property> <name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name> <value>file:///usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name> <value>file:///usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/datanode</value> </property> </configuration>
Now, the Hadoop filesystem needs to be formatted so that we can start to use it. The format command should be issued with write permission since it creates current directory under /usr/local/hadoop_store/hdfs/namenode folder:
hduser@k:~$ hadoop namenode -format DEPRECATED: Use of this script to execute hdfs command is deprecated. Instead use the hdfs command for it. 14/07/13 22:13:05 INFO namenode.NameNode: STARTUP_MSG: /************************************************************ STARTUP_MSG: Starting NameNode STARTUP_MSG: host = k/127.0.1.1 STARTUP_MSG: args = [-format] STARTUP_MSG: version = 2.4.1 STARTUP_MSG: classpath = /usr/local/hadoop/etc/hadoop:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/common/lib/netty-3.6.2.Final.jar:/usr/local/hadoop ... common-2.4.1.jar:/usr/local/hadoop/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-client-app-2.4.1.jar:/contrib/capacity-scheduler/*.jar:/contrib/capacity-scheduler/*.jar STARTUP_MSG: build = http://svn.apache.org/repos/asf/hadoop/common -r 1604318; compiled by 'jenkins' on 2014-06-21T05:43Z STARTUP_MSG: java = 1.7.0_55 ************************************************************/ 14/07/13 22:13:05 INFO namenode.NameNode: registered UNIX signal handlers for [TERM, HUP, INT] 14/07/13 22:13:05 INFO namenode.NameNode: createNameNode [-format] 14/07/13 22:13:07 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable Formatting using clusterid: CID-cea08f18-e94e-49c7-b380-9c55ea473122 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: fsLock is fair:true 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.HostFileManager: read includes: HostSet( ) 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.HostFileManager: read excludes: HostSet( ) 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.DatanodeManager: dfs.block.invalidate.limit=1000 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.DatanodeManager: dfs.namenode.datanode.registration.ip-hostname-check=true 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map BlocksMap 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO util.GSet: 2.0% max memory 889 MB = 17.8 MB 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^21 = 2097152 entries 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: dfs.block.access.token.enable=false 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: defaultReplication = 1 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: maxReplication = 512 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: minReplication = 1 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: maxReplicationStreams = 2 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: shouldCheckForEnoughRacks = false 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: replicationRecheckInterval = 3000 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: encryptDataTransfer = false 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO blockmanagement.BlockManager: maxNumBlocksToLog = 1000 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: fsOwner = hduser (auth:SIMPLE) 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: supergroup = supergroup 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: isPermissionEnabled = true 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: HA Enabled: false 14/07/13 22:13:08 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Append Enabled: true 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map INodeMap 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: 1.0% max memory 889 MB = 8.9 MB 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^20 = 1048576 entries 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.NameNode: Caching file names occuring more than 10 times 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map cachedBlocks 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: 0.25% max memory 889 MB = 2.2 MB 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^18 = 262144 entries 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: dfs.namenode.safemode.threshold-pct = 0.9990000128746033 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: dfs.namenode.safemode.min.datanodes = 0 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: dfs.namenode.safemode.extension = 30000 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Retry cache on namenode is enabled 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.FSNamesystem: Retry cache will use 0.03 of total heap and retry cache entry expiry time is 600000 millis 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: Computing capacity for map NameNodeRetryCache 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: VM type = 64-bit 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: 0.029999999329447746% max memory 889 MB = 273.1 KB 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO util.GSet: capacity = 2^15 = 32768 entries 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.AclConfigFlag: ACLs enabled? false 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO namenode.FSImage: Allocated new BlockPoolId: BP-158368351-127.0.1.1-1405314789318 14/07/13 22:13:09 INFO common.Storage: Storage directory /app/hadoop/tmp/dfs/name has been successfully formatted. 14/07/13 22:13:10 INFO namenode.NNStorageRetentionManager: Going to retain 1 images with txid >= 0 14/07/13 22:13:10 INFO util.ExitUtil: Exiting with status 0 14/07/13 22:13:10 INFO namenode.NameNode: SHUTDOWN_MSG: /************************************************************ SHUTDOWN_MSG: Shutting down NameNode at k/127.0.1.1 ************************************************************/
Everything seems to be working except:
...WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
The reason we have that warning is the native Hadoop library $HADOOP_HOME/lib/native/libhadoop.so.1.0.0 was actually compiled on 32 bit while my machine is 64bit. Because it's just a warning, and won't impact Hadoop's functionalities, we can move on.
Note that hadoop namenode -format command should be executed once before we start using Hadoop. If this command is executed again after Hadoop has been used, it'll destroy all the data on the Hadoop file system.
Now it's time to start the newly installed single node cluster. We can use start-all.sh or (start-dfs.sh and start-yarn.sh)
hduser@k:/home/k$ start-all.sh This script is Deprecated. Instead use start-dfs.sh and start-yarn.sh 14/07/13 23:36:59 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable Starting namenodes on [localhost] localhost: starting namenode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hduser-namenode-k.out localhost: starting datanode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hduser-datanode-k.out Starting secondary namenodes [0.0.0.0] 0.0.0.0: starting secondarynamenode, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/hadoop-hduser-secondarynamenode-k.out 14/07/13 23:37:40 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable starting yarn daemons starting resourcemanager, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/yarn-hduser-resourcemanager-k.out localhost: starting nodemanager, logging to /usr/local/hadoop/logs/yarn-hduser-nodemanager-k.out
We can check if it's really up and running:
hduser@k:/home/k$ jps 6129 Jps 5484 NameNode 5811 SecondaryNameNode 5969 ResourceManager 6094 NodeManager 5610 DataNode
The output means that we now have a functional instance of Hadoop running on our VPS (Virtual private server).
Another way to check is using netstat:
hduser@k:/home/k$ netstat -plten | grep java (Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.) tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8033 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 159850 5969/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50020 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 148236 5610/java tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:54310 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 148539 5484/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8040 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 159245 6094/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8042 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 158297 6094/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50090 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 150200 5811/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50070 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 143035 5484/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8088 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 159251 5969/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:42586 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 158283 6094/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50010 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 146772 5610/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:50075 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 147223 5610/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8030 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 159215 5969/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8031 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 154756 5969/java tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:8032 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002 159228 5969/java
$ pwd /usr/local/hadoop/sbin $ ls distribute-exclude.sh httpfs.sh start-all.sh start-yarn.cmd stop-dfs.cmd yarn-daemon.sh hadoop-daemon.sh mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start-balancer.sh start-yarn.sh stop-dfs.sh yarn-daemons.sh hadoop-daemons.sh refresh-namenodes.sh start-dfs.cmd stop-all.cmd stop-secure-dns.sh hdfs-config.cmd slaves.sh start-dfs.sh stop-all.sh stop-yarn.cmd hdfs-config.sh start-all.cmd start-secure-dns.sh stop-balancer.sh stop-yarn.sh
We run stop-all.sh or (stop-dfs.sh and stop-yarn.sh) to stop all the daemons running on our machine:
$ /usr/local/hadoop/sbin/stop-all.sh This script is Deprecated. Instead use stop-dfs.sh and stop-yarn.sh 14/07/13 20:55:59 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable Stopping namenodes on [localhost] localhost: no namenode to stop localhost: stopping datanode Stopping secondary namenodes [0.0.0.0] 0.0.0.0: stopping secondarynamenode 14/07/13 20:56:24 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable stopping yarn daemons stopping resourcemanager localhost: stopping nodemanager no proxyserver to stop
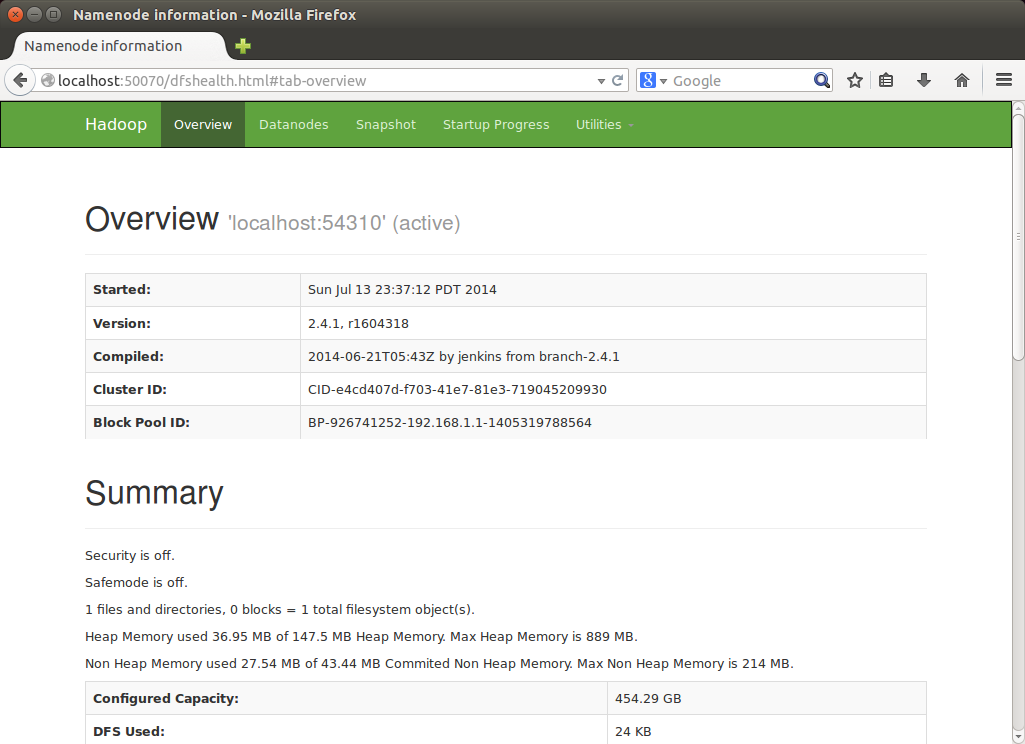
http://localhost:50070/ - web UI of the NameNode daemon
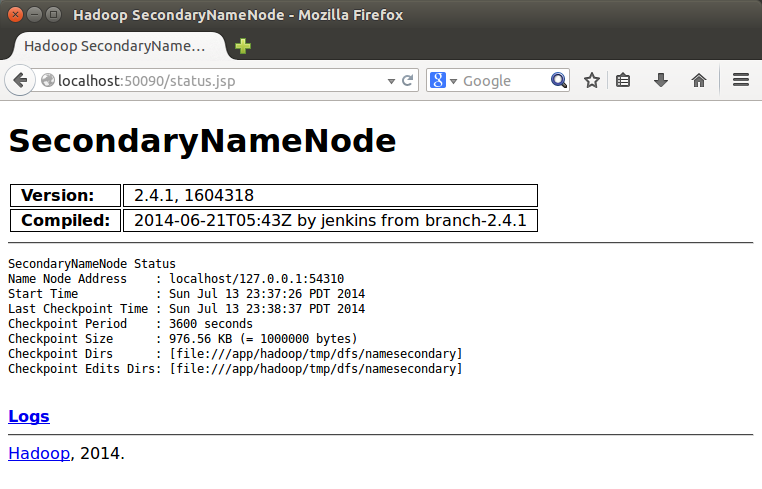
SecondaryNameNode
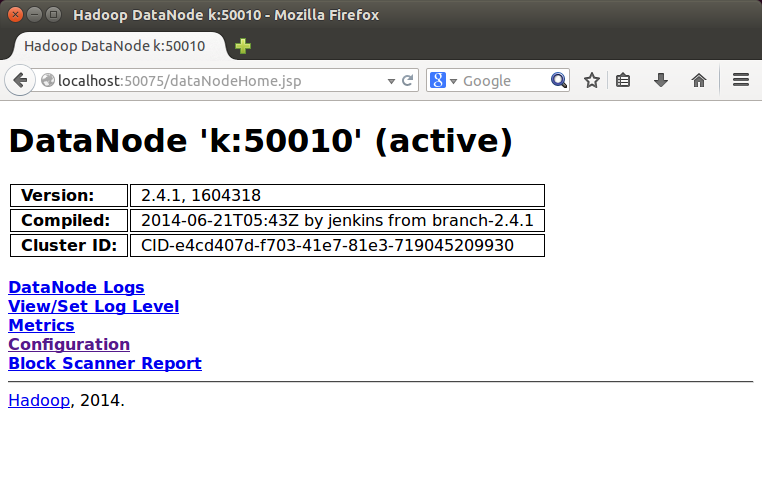
DataNode
If we have an application that is set up to use Hadoop, we can fire that up and start using it with our Hadoop installation!