Docker Q & A
Difference between Docker Image and container.
If a Docker application works on our local computer, it'll work anywhere that supports Docker. It greatly simplifies development process and can be a powerful tool for continuous delivery.
To understand Docker, we need to know two key facets of how Docker works. Docker image vs container!
Docker image is a kind of snapshot. We can think of it as a picture of a Docker virtual machine and the container is the virtual machine.
A container is an instance of a docker image. In other words, a running instance of an image is a container. We can see all our images with
docker images:$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE mysql latest 8457e9155715 9 days ago 546MB busybox latest 491198851f0c 2 weeks ago 1.23MB ubuntu 18.04 c090eaba6b94 6 weeks ago 63.3MB
To see our running containers with
docker ps:$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2666137d9726 busybox "sh" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours tender_jones 55ae35026d6c ubuntu:18.04 "/bin/bash" 6 days ago Up 6 days laughing_mcclintock
To see all containers including the ones stopped, we can use
docker ps -a:$ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 5f6afe49bbd0 mysql "docker-entrypoint.s…" About a minute ago Exited (0) 7 seconds ago angry_jang 2666137d9726 busybox "sh" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours tender_jones 55ae35026d6c ubuntu:18.04 "/bin/bash" 6 days ago Up 6 days laughing_mcclintockWhat is a Dockerfile?
In order to build the application, we need to use a Dockerfile.
In cooking, we need a recipe to make cookies. In Docker, we need a Dockerfile to build an image.
A Dockerfile is simply a text-based script of instructions that is used to create a container image. Basically, it contains all the possible commands that a user may call on the command line to create an image.
To see how it works, we'll use https://github.com/docker/getting-started.
$ git clone https://github.com/docker/getting-started/tree/master/app $ tree ../getting-started -L 2 ../getting-started ├── Jenkinsfile ├── LICENSE ├── README.md ├── app │ ├── package.json │ ├── spec │ ├── src │ └── yarn.lock ├── build.sh ├── docker-compose.yml ├── docs │ ├── css │ ├── fonts │ ├── images │ ├── index.md │ └── tutorial ├── mkdocs.yml ├── requirements.txt └── yarn.lock
-
Create a file named Dockerfile in the same folder as the file package.json with the following contents:
FROM node:12-alpine WORKDIR /app COPY . . RUN yarn install --production CMD ["node", "src/index.js"]
-
Go to the app directory with the Dockerfile and build the container image using the
docker buildcommand:~/getting-started/app $ ls Dockerfile package.json spec src yarn.lock ~/getting-started/app $ docker build -t getting-started . $ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE getting-started latest 295a1b181e50 22 minutes ago 179MB
Here, we instructed the builder that we wanted to start from the node:12-alpine image. The WORKDIR command is used to define the working directory of a Docker container at any given time. Any RUN, CMD, ADD, COPY, or ENTRYPOINT command will be executed in the specified working directory.
After the image was downloaded, we copied in our application and used
yarnto install our application's dependencies. TheCMDspecifies the default command to run when starting a container from this image.The -t flag tags our image to give it a human-readable name. Since we named the image getting-started, we can refer to that image when we run a container.
The . at the end of the
docker buildcommand tells that Docker should look for the Dockerfile in the current directory.Now that we have an image, it's time to run the application using
docker runcommand:$ docker run -d -p 3000:3000 getting-started 57198610f11c45a9eb4b7fd64fd93eabc2e0cbae17f980a8492618cb9822ba3f
Note that we're running the new container in "detached" mode (in the background) and creating a mapping between the host's port 3000 to the container's port 3000. Without the port mapping, we wouldn't be able to access the application.
-
Open a web browser to http://localhost:3000. We should see our app:
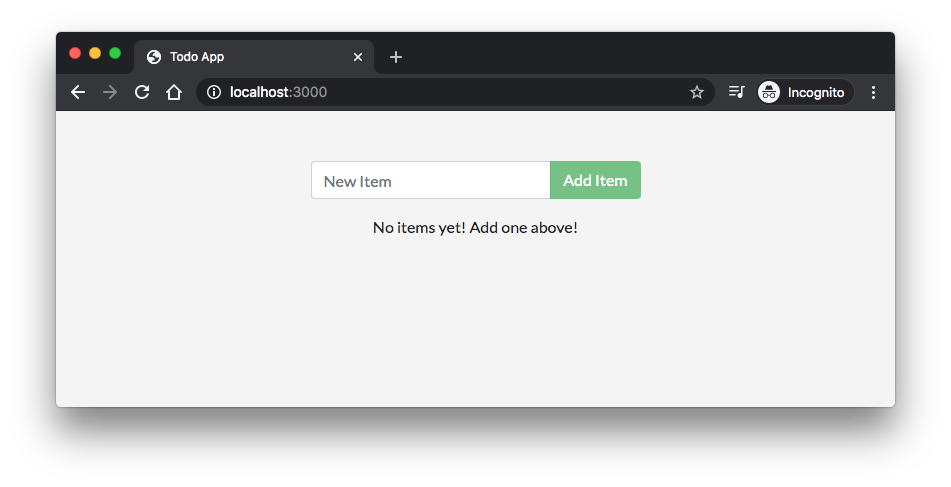
-
One more thing about the
CMDinstruction: the difference between theCMDandENTRYPOINTwith related to the supplied to the docker run command. While the CMD will be completely over-written by the supplied command (or args), for theENTRYPOINT, the supplied command will be appended to it (Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT).The Dockfile can be re-written as the following:
FROM node:12-alpine WORKDIR /app COPY . . RUN yarn install --production ENTRYPOINT ["node"] CMD ["src/index.js"]
With the new Dockerfile, we can pass an arg to our
docker runcommand, for example:$ docker run -d -p 3000:3000 getting-started src/index.js c85168de055f81f4390693c8029699266e69d304cdaf10e3c1c5a60d37040739
Here, though we used the same arg, as in
CMD ["src/index.js"], we could overwrite the arg provided by theCMDinstruction. - Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
For more about Dockerfile instructions, checkout the following list:
-
Preferred way of removing containers?
Let's stop the "busybox" container. First we need to do
docker stop:$ docker stop 2666137d9726 2666137d9726
and then followed by adocker rm:$ docker rm 2666137d9726 2666137d9726Difference between Docker pause and stop.
$ docker run -it -d --name=busybox1 busybox /bin/sh 007d5db147718b9fe6e2d2d4054fc6e1683836a74c4df11d08458e7d2a7e7018 $ docker run -it -d --name=busybox2 busybox /bin/sh d00834397e505f86979ede9c9bd97bc2d4945d3f0c8f8486721a04165661ec68 $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES d00834397e50 busybox "/bin/sh" 4 seconds ago Up 4 seconds busybox2 007d5db14771 busybox "/bin/sh" 13 seconds ago Up 13 seconds busybox1
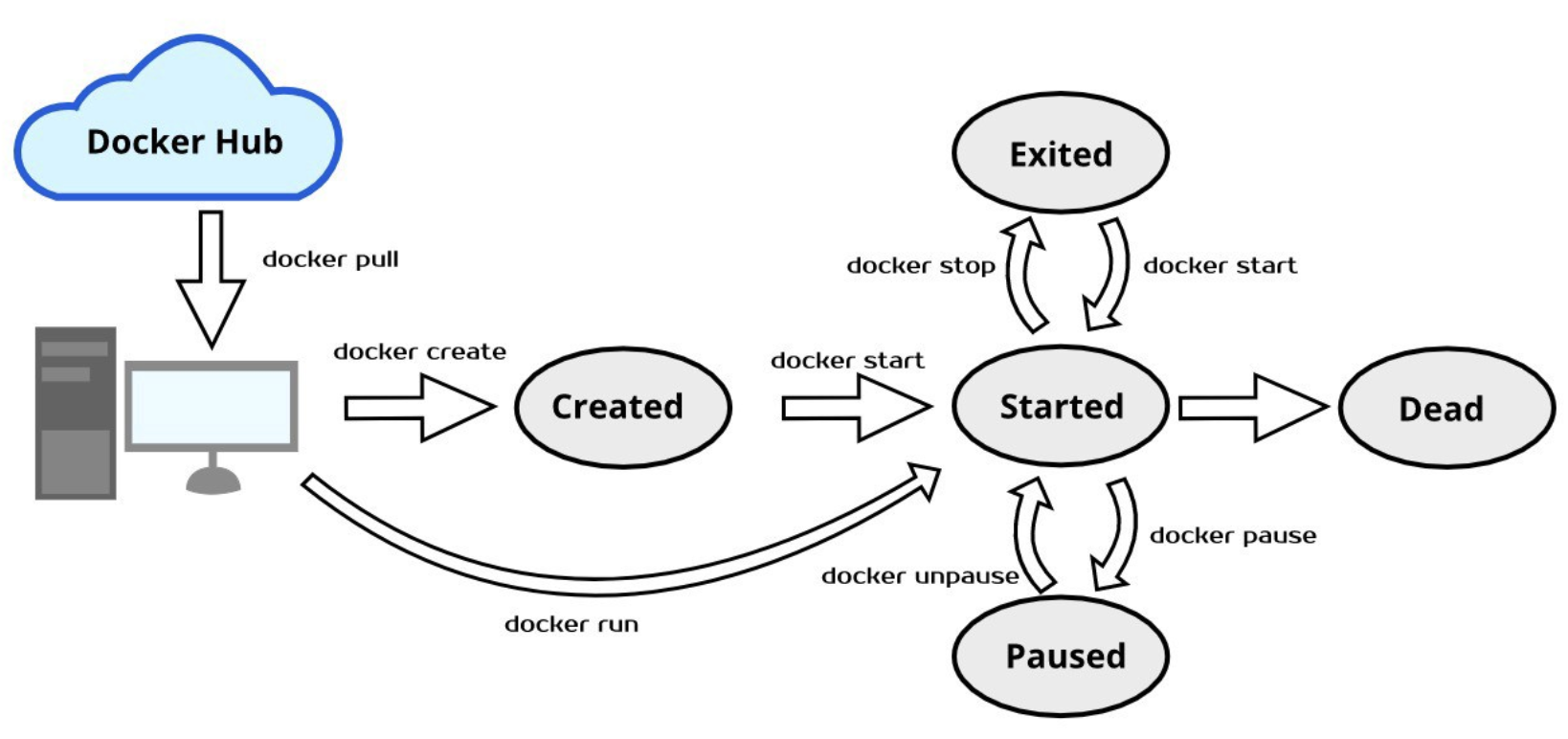
Picture credit: Get Started with Docker Lifecycle
We can stop the "busybox1" and pause the "busybox2":
$ docker stop busybox1 busybox1 $ docker pause busybox2 busybox2 $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 21f6d14521b8 busybox "/bin/sh" 22 minutes ago Up 45 seconds (Paused) busybox2
The
docker pausecommand suspends (via SIGSTOP signal) all processes in the specified containers.The
docker stopcommand. The main process inside the container will receive SIGTERM, and after a grace period, SIGKILL.We cannot remove a paused container.
$ docker rm busybox2 Error response from daemon: You cannot remove a paused container 21f6d14521b8c16455166536000634e66097c7915f7608718e773e58e4e7aacf. Unpause and then stop the container before attempting removal or force remove
SIGSTOP is the pause signal that cannot be caught or ignored. The shell uses pausing (and its counterpart, resuming via SIGCONT) to implement job control.
$ docker restart busybox2 busybox2 $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 21f6d14521b8 busybox "/bin/sh" About an hour ago Up 5 seconds busybox2 55ae35026d6c ubuntu:18.04 "/bin/bash" 6 days ago Up 6 days laughing_mcclintock
- How can we create a Docker container in the Stopped state?
$ docker create --name MyContainer ubuntu 692b7ce25a7743907be877e7a758fd6a16b390a09275d73ade607dd25c4b0ee9
We can see that it has created a new container. But we won’t see MyContainer because though it was created, it was never started.
$ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 692b7ce25a77 ubuntu "/bin/bash" 2 minutes ago Created MyContainer
We can start this container with
docker startcommand:$ docker start MyContainer MyContainer
docker stats:The docker stats command returns a live data stream for running containers.
$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES c85168de055f getting-started "node src/index.js" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:3000->3000/tcp modest_easley 55ae35026d6c ubuntu:18.04 "/bin/bash" 8 days ago Up 8 days laughing_mcclintock $ docker stats CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS c85168de055f modest_easley 0.00% 16.38MiB / 2.434GiB 0.66% 11.2kB / 5.41kB 0B / 0B 11 55ae35026d6c laughing_mcclintock 0.00% 1.125MiB / 2.434GiB 0.05% 14.9kB / 0B 0B / 0B 1 $ docker stats c85168de055f CONTAINER ID NAME CPU % MEM USAGE / LIMIT MEM % NET I/O BLOCK I/O PIDS c85168de055f modest_easley 0.00% 16.38MiB / 2.434GiB 0.66% 11.3kB / 5.41kB 0B / 0B 11
docker system prune:It's a command used to remove all stopped containers, unused networks, build caches, and dangling images. The
pruneis one of the most useful commands in Docker:$ docker system prune WARNING! This will remove: - all stopped containers - all networks not used by at least one container - all dangling images - all dangling build cache Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y Deleted Containers: 1470e09b748c5a89a41a415d4bdfbeec61e4091d38eaceef94c96ac9edb90469 692b7ce25a7743907be877e7a758fd6a16b390a09275d73ade607dd25c4b0ee9 ... Deleted Images: deleted: sha256:295a1b181e50c37a3a9595bd498b5c980a9f90823473abdb8704ce3308628eef deleted: sha256:77234e845dbed0075aecab391e14bb9f1a34ec7bd34b88284d2f74b31b9837b0 ... Total reclaimed space: 89.85MB
docker-compose:
Most of the time, we will most likely want to bring up all of the services listed in our docker-compose.yml and have the containers run their default command, so we would want to use
docker-compose up.The
docker-compose runcommand will spin up a new container for us to use while thedocker-compose execcommand will allow us to use a container that is already running.Multistage Image Builds:
While using containers to build applications can be useful, it is important to distinguish between the build image and the runtime image.
The build image contains all the tooling and libraries that are necessary to compile the application, while the runtime image contains the application to be deployed. A Java application has a build image that contains the JDK, Gradle/Maven, and compilation and testing tooling. Then our runtime image can contain only the Java runtime and our application.Compiling code as part of the image build is the most common ways of accidentally building large images.
To resolve this issue, Docker introduced multistage builds. Rather than producing a single image, with the multistage builds, a Docker file can actually produce multiple images where each image is considered a stage. Artifacts can be copied from preceding stages to the current stage.
The following two Dockerfiles demonstrate the multistage image builds from Use multi-stage builds:
Dockerfile with number:FROM golang:1.7.3 WORKDIR /go/src/github.com/alexellis/href-counter/ RUN go get -d -v golang.org/x/net/html COPY app.go . RUN CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux go build -a -installsuffix cgo -o app . FROM alpine:latest RUN apk --no-cache add ca-certificates WORKDIR /root/ COPY --from=0 /go/src/github.com/alexellis/href-counter/app . CMD ["./app"]
The second FROM instruction starts a new build stage with the alpine:latest image as its base. The
COPY --from=0line copies just the built artifact from the previous stage into this new stage. The Go SDK and any intermediate artifacts are left behind, and not saved in the final image.
Dockerfile with name:FROM golang:1.7.3 AS builder WORKDIR /go/src/github.com/alexellis/href-counter/ RUN go get -d -v golang.org/x/net/html COPY app.go . RUN CGO_ENABLED=0 GOOS=linux go build -a -installsuffix cgo -o app . FROM alpine:latest RUN apk --no-cache add ca-certificates WORKDIR /root/ COPY --from=builder /go/src/github.com/alexellis/href-counter/app . CMD ["./app"]
By default, the stages are not named, and we refer to them by their integer number, starting with 0 for the first
FROMinstruction as shown in the first Dockerfile. However, we can name our stages, by adding anAS <NAME>to theFROMinstruction. The 2nd example improves the 1st one by naming the stages and using the name in theCOPYinstruction.
Here is another sample that builds a "Go" application and runs the app.
hello.go:
package main import ( "fmt" "log" "net/http" ) //Hello Server responds to requests with the given URL path. func HelloServer(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello, you requested: %s", r.URL.Path) log.Printf("Received request for path: %s", r.URL.Path) } func main() { var addr string = ":8181" handler := http.HandlerFunc(HelloServer) if err := http.ListenAndServe(addr, handler); err != nil { log.Fatalf("Could not listen on port %s %v", addr, err) } }
Dockerfile that builds the app then copy the binary into a container:
FROM golang:1-alpine as build WORKDIR /app COPY hello.go /app RUN go build hello.go FROM alpine:latest WORKDIR /app COPY --from=build /app /app EXPOSE 8180 ENTRYPOINT ["./hello"]
Now, we have the following files in our working directory:
$ ls Dockerfile hello.go
We are now ready to build the image from the Dockerfile:
$ docker build -t hello-go . Sending build context to Docker daemon 3.072kB Step 1/9 : FROM golang:1-alpine as build ---> 14ee78639386 Step 2/9 : WORKDIR /app ---> Using cache ---> 295af3c2ffa0 Step 3/9 : COPY hello.go /app ---> Using cache ---> debfbdb3c01d Step 4/9 : RUN go build hello.go ---> Using cache ---> e29f2ba09000 Step 5/9 : FROM alpine:latest ---> 49f356fa4513 Step 6/9 : WORKDIR /app ---> Running in 034e0cf20138 Removing intermediate container 034e0cf20138 ---> 03048fdf20d8 Step 7/9 : COPY --from=build /app /app ---> f496e0e4bbcb Step 8/9 : EXPOSE 8180 ---> Running in 7f2b631302e1 Removing intermediate container 7f2b631302e1 ---> c1545d176662 Step 9/9 : ENTRYPOINT ["./hello"] ---> Running in dfeb253925e1 Removing intermediate container dfeb253925e1 ---> 10456b843247 Successfully built 10456b843247 Successfully tagged hello-go:latest $ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-go latest 10456b843247 About a minute ago 11.8MB
To run the container and expose the internal port 8181 to our host port 8182:
$ docker run -d --name hello-go-container --rm -p 8182:8181 hello-go 907ad5290aa7a2db70496082906d25a291a5077933d343f6a8a7d50efa0760c7 $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 907ad5290aa7 hello-go "./hello" 16 seconds ago Up 15 seconds 8180/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8182->8181/tcp hello-go-container
Test the application:
$ curl localhost:8182 Hello, you requested: /
It appears to be working fine!
One more step. Let's go into the container and check the /app folder:
$ docker exec -it hello-go-container /bin/sh /app # ls -la total 6044 drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Apr 6 23:47 . drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Apr 6 23:53 .. -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 6176661 Apr 6 21:23 hello -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 493 Apr 6 20:22 hello.go
As we can see the binary (hello) has been copied successfully from build stage to the last stage.
Sometimes when we run a docker container it exits immediately. Why?
The short answer is that the container exits because it has no process to run.
In this section, we'll also learn the difference between
CMDandENTRYPOINTWhen we run an Ubuntu image, it exits immediately as we can see below:
$ docker run ubuntu:18.04 Unable to find image 'ubuntu:18.04' locally 18.04: Pulling from library/ubuntu 6cf436f81810: Pull complete 987088a85b96: Pull complete b4624b3efe06: Pull complete d42beb8ded59: Pull complete Digest: sha256:7a47ccc3bbe8a451b500d2b53104868b46d60ee8f5b35a24b41a86077c650210 Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:18.04 $ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 9ba1aa158caf ubuntu:18.04 "/bin/bash" 11 seconds ago Exited (0) 10 seconds ago youthful_stonebraker
Why is that? Why it exited?
Unlike VMs which are meant to host OS, containers are meant to run a task or a process such as a web server/application or a db. So, once a task is complete, a container exits. A container lives as long as a process within it is running. If an application in a container crashes, container exits.
So, who defines which process should be running inside a container?
Let's look into the following Dockerfile for nginx, specially the CMD[] instruction:
# # Nginx Dockerfile # # https://github.com/dockerfile/nginx # # Pull base image. FROM dockerfile/ubuntu # Install Nginx. RUN \ add-apt-repository -y ppa:nginx/stable && \ apt-get update && \ apt-get install -y nginx && \ rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && \ echo "\ndaemon off;" >> /etc/nginx/nginx.conf && \ chown -R www-data:www-data /var/lib/nginx # Define mountable directories. VOLUME ["/etc/nginx/sites-enabled", "/etc/nginx/certs", "/etc/nginx/conf.d", "/var/log/nginx", "/var/www/html"] # Define working directory. WORKDIR /etc/nginx # Define default command. CMD ["nginx"] # Expose ports. EXPOSE 80 EXPOSE 443
Yes, the CMD[] tells the Docker which program should be run when the container starts. In our case, it is the "nginx" command.
For mysql Dockerfile it is mysqld command:
COPY docker-entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh COPY healthcheck.sh /healthcheck.sh ENTRYPOINT ["/entrypoint.sh"] HEALTHCHECK CMD /healthcheck.sh EXPOSE 3306 33060 CMD ["mysqld"]
How about our Ubuntu image Dockerfile?
... CMD ["/bin/bash"]
It uses bash for its default command.
Unlike the web server or a db, the bash is not a process, it's just a shell listening and waiting for an input. If it does not get any from a terminal, it exits.
Earlier, when we run a container from the Ubuntu image, it launches a "bash" program but the Docker, by default, not attaching any terminal to a container when it runs. So, the container could not find a terminal, and just exited.
We can make container alive for a while by overwriting the CMD ["/bin/bash"], for example, sleep 30s when we run docker:
$ docker run ubuntu:18.04 sleep 30s $ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 55ab52fa884d ubuntu:18.04 "sleep 30s" 7 seconds ago Up 6 seconds relaxed_euler
But how we can make the container always run the
sleepcommand when it starts? Note that we added it to thedocker runcommand.One way to avoid adding the "sleep 30s" after the command is to use the
CMDinstruction in our Dockerfile:FROM ubuntu:18.04 CMD sleep 30
Or we can use array:
FROM ubuntu:18.04 CMD ["sleep", "30"]
Note that we should NOT use the following because the command and args should be separated:
CMD ["sleep 30"] X
Now we can build our image with a name of "ubuntu-sleep":
$ docker build -t ubuntu-sleep . Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.048kB Step 1/2 : FROM ubuntu:18.04 ---> 47b19964fb50 Step 2/2 : CMD ["sleep", "30"] ---> Running in c84ecc7a5b3d Removing intermediate container c84ecc7a5b3d ---> 3f21ee94c150 Successfully built 3f21ee94c150 Successfully tagged ubuntu-sleep:latest
Then, run a container from the newly created image:
$ docker run ubuntu-sleep
The container always sleeps 30s after it started!
But we have a problem. What if we want to change the sleep time?
Currently, it's been hard-coded.
Of course, we can overwrite the command like this:
$ docker run ubuntu-sleep sleep 5
However, because the image name itself is already indicating it would sleep, we need to find a way of just feeding the seconds as an argument not with the
sleepcommand, and the image automatically invoke the "sleep" command needing only the parameter. Something like this:$ docker run ubuntu-sleep 5
That's why we need the
ENTRYPOINTinstruction.It simply specifies a program to run when a container starts.
So, our Dockerfile should be changed from:
FROM ubuntu:18.04 CMD ["sleep", "30"]
to:
FROM ubuntu:18.04 ENTRYPOINT ["sleep"]
Build a new image and run the container:
$ docker build -t ubuntu-sleep . Sending build context to Docker daemon 2.048kB Step 1/2 : FROM ubuntu:18.04 ---> 47b19964fb50 Step 2/2 : ENTRYPOINT ["sleep"] ---> Running in e5e6e83e9e01 Removing intermediate container e5e6e83e9e01 ---> affbc2e6ed86 Successfully built affbc2e6ed86 Successfully tagged ubuntu-sleep:latest $ docker run ubuntu-sleep 5
Note the difference between the
CMDandENTRYPOINTwith related to the supplied to thedocker runcommand. While theCMDwill be completely over-written by the supplied command (or args), for theENTRYPOINT, the supplied command will be appended to it.Another problem in our Dockerfile: let's see:
$ docker run ubuntu-sleep sleep: missing operand Try 'sleep --help' for more information.
In the command above, we did not supply an arg for the
sleepcommand, and got an error when the container started.We need a default value for the command so that container runs event though an arg is missing.
Here is where the
CMDcomes into play: theCMDinstruction will be appended to theENTRYPOINTinstruction.Here is our new Dockerfile:
FROM ubuntu:18.04 ENTRYPOINT ["sleep"] CMD ["5"]
Build the image and run a container from the image, and we should not get any error when we do not specify sleep time:
$ docker build -t ubuntu-sleep . $ docker run ubuntu-sleep
If we add a parameter to the command, it will overwrites the default value specified in
CMD.One more thing regarding the
ENTRYPOINT. What if we want to override the command specified in theENTRYPOINT?In that case, we can give a new command in
docker runcommand, for example:$ docker run --entrypoint new-sleep-command ubuntu-sleep 60
Let's go further and look into how the
ENTRYPOINTandCMDin Dockerfile are translated in a Pod definition yaml file: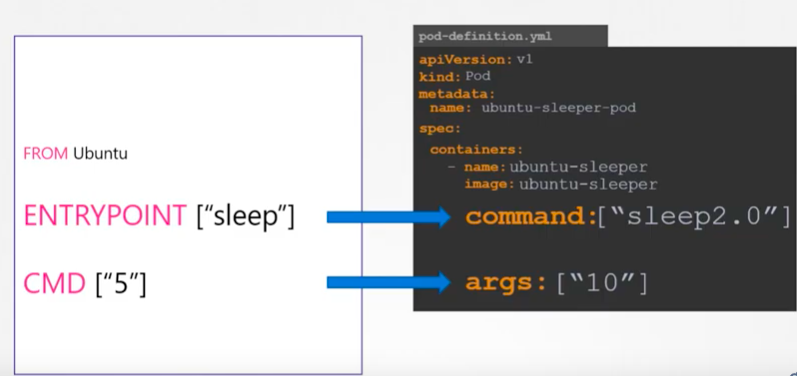
Picture source Docker for Beginners - Commands vs Entrypoint - Kubernetes
As we can see the parameters in
ENTRYPOINTandCMDcan be overwritten with the ones provided via "command" are "args" in "spec.containers" of the yaml.
How we can run a container with "root" privilege?
$ docker exec -u 0 -it my-container sh
How to push an image to AWS ECR?
Docker login first assuming the AWS credentials are in place either from ENV or from ~/.aws/credentials:
$ aws --region us-west-2 ecr get-login-password \ | docker login \ --password-stdin \ --username AWS \ 437028470429.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com Login Succeeded
Then, push it to ECR:
$ docker push 437028470429.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/test-khong:0.2.1 The push refers to repository [437028470429.dkr.ecr.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/test-khong] ... 0.2.1: digest: sha256:ca2fc17f610...2ceaddf5e0cbda5e74 size: 4484
Docker & K8s
- Docker install on Amazon Linux AMI
- Docker install on EC2 Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker container vs Virtual Machine
- Docker install on Ubuntu 14.04
- Docker Hello World Application
- Nginx image - share/copy files, Dockerfile
- Working with Docker images : brief introduction
- Docker image and container via docker commands (search, pull, run, ps, restart, attach, and rm)
- More on docker run command (docker run -it, docker run --rm, etc.)
- Docker Networks - Bridge Driver Network
- Docker Persistent Storage
- File sharing between host and container (docker run -d -p -v)
- Linking containers and volume for datastore
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically I - FROM, MAINTAINER, and build context
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically II - revisiting FROM, MAINTAINER, build context, and caching
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically III - RUN
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically IV - CMD
- Dockerfile - Build Docker images automatically V - WORKDIR, ENV, ADD, and ENTRYPOINT
- Docker - Apache Tomcat
- Docker - NodeJS
- Docker - NodeJS with hostname
- Docker Compose - NodeJS with MongoDB
- Docker - Prometheus and Grafana with Docker-compose
- Docker - StatsD/Graphite/Grafana
- Docker - Deploying a Java EE JBoss/WildFly Application on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Using Docker Containers
- Docker : NodeJS with GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker : Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline with Jenkinsfile and Github
- Docker : Jenkins Master and Slave
- Docker - ELK : ElasticSearch, Logstash, and Kibana
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elasticsearch on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Filebeat on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Logstash on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Kibana on Centos 7
- Docker - ELK 7.6 : Elastic Stack with Docker Compose
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) via Elasticsearch operator on minikube
- Docker - Deploy Elastic Stack via Helm on minikube
- Docker Compose - A gentle introduction with WordPress
- Docker Compose - MySQL
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services
- MEAN Stack app on Docker containers : micro services via docker-compose
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part A (install vault, unsealing, static secrets, and policies)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part B (EaaS, dynamic secrets, leases, and revocation)
- Docker Compose - Hashicorp's Vault and Consul Part C (Consul)
- Docker Compose with two containers - Flask REST API service container and an Apache server container
- Docker compose : Nginx reverse proxy with multiple containers
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Getting started
- Docker & Kubernetes : Envoy - Front Proxy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ambassador - Envoy API Gateway on Kubernetes
- Docker Packer
- Docker Cheat Sheet
- Docker Q & A #1
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part I
- Kubernetes Q & A - Part II
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker
- Docker - Run a React app in a docker II (snapshot app with nginx)
- Docker - NodeJS and MySQL app with React in a docker
- Docker - Step by Step NodeJS and MySQL app with React - I
- Installing LAMP via puppet on Docker
- Docker install via Puppet
- Nginx Docker install via Ansible
- Apache Hadoop CDH 5.8 Install with QuickStarts Docker
- Docker - Deploying Flask app to ECS
- Docker Compose - Deploying WordPress to AWS
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI EC2 type)
- Docker - WordPress Deploy to ECS with Docker-Compose (ECS-CLI Fargate type)
- Docker - ECS Fargate
- Docker - AWS ECS service discovery with Flask and Redis
- Docker & Kubernetes : minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes 2 : minikube Django with Postgres - persistent volume
- Docker & Kubernetes 3 : minikube Django with Redis and Celery
- Docker & Kubernetes 4 : Django with RDS via AWS Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kops on AWS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Ingress controller on AWS with Kops
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : HashiCorp's Vault and Consul - Auto-unseal using Transit Secrets Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes & Persistent Volumes Claims - hostPath and annotations
- Docker & Kubernetes : Persistent Volumes - Dynamic volume provisioning
- Docker & Kubernetes : DaemonSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Secrets
- Docker & Kubernetes : kubectl command
- Docker & Kubernetes : Assign a Kubernetes Pod to a particular node in a Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : Configure a Pod to Use a ConfigMap
- AWS : EKS (Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Run a React app in a minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Minikube install on AWS EC2
- Docker & Kubernetes : Cassandra with a StatefulSet
- Docker & Kubernetes : Terraform and AWS EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Pods and Service definitions
- Docker & Kubernetes : Service IP and the Service Type
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes DNS with Pods and Services
- Docker & Kubernetes : Headless service and discovering pods
- Docker & Kubernetes : Scaling and Updating application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Horizontal pod autoscaler on minikubes
- Docker & Kubernetes : From a monolithic app to micro services on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Rolling updates
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deployments to GKE (Rolling update, Canary and Blue-green deployments)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Slack Chat Bot with NodeJS on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery with Jenkins Multibranch Pipeline for Dev, Canary, and Production Environments on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : NodePort vs LoadBalancer vs Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB / MongoExpress on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Load Testing with Locust on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : MongoDB with StatefulSets on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up Ingress with NGINX Controller on Minikube (Mac)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller for Dashboard service on Minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : Nginx Ingress Controller on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Ingress with AWS ALB Ingress Controller in EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Setting up a private cluster on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Kubernetes Namespaces (default, kube-public, kube-system) and switching namespaces (kubens)
- Docker & Kubernetes : StatefulSets on minikube
- Docker & Kubernetes : RBAC
- Docker & Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, and IAM
- Docker & Kubernetes - Kubernetes Service Account, RBAC, IAM with EKS ALB, Part 1
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : My first Helm deploy
- Docker & Kubernetes : Readiness and Liveness Probes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm chart repository with Github pages
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB with Ingress to Minikube using Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 2 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying WordPress and MariaDB to AWS using Helm 3 Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Chart for Node/Express and MySQL with Ingress
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using Helm and Prometheus Operator - Monitoring Kubernetes node resources out of the box
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploy Prometheus and Grafana using kube-prometheus-stack Helm Chart
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio (service mesh) sidecar proxy on GCP Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : Istio on Minikube with AWS EC2 for Bookinfo Application
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part I)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying .NET Core app to Kubernetes Engine and configuring its traffic managed by Istio (Part II - Prometheus, Grafana, pin a service, split traffic, and inject faults)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Helm Package Manager with MySQL on GCP Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Deploying Memcached on Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : EKS Control Plane (API server) Metrics with Prometheus
- Docker & Kubernetes : Spinnaker on EKS with Halyard
- Docker & Kubernetes : Continuous Delivery Pipelines with Spinnaker and Kubernetes Engine
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-dind (docker-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : Multi-node Local Kubernetes cluster : Kubeadm-kind (k8s-in-docker)
- Docker & Kubernetes : nodeSelector, nodeAffinity, taints/tolerations, pod affinity and anti-affinity - Assigning Pods to Nodes
- Docker & Kubernetes : Jenkins-X on EKS
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD App of Apps with Heml on Kubernetes
- Docker & Kubernetes : ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster
- Docker & Kubernetes : GitOps with ArgoCD for Continuous Delivery to Kubernetes clusters (minikube) - guestbook
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization