Screen capture, recording, casting A - 2020

In this chapter, we want to record the screen of our desktop running Ubuntu 13.1.
We'll use the FFmpeg's x11grab, a module for screen capture. This method known for giving the best results for capturing screen and is one of the the most flexible methods. It allows us to use a variety of inputs and output formats.
Because doing both of recording and compressing takes time and computing power, we may want to do it in two steps:
- Capture a lossless video.
- Encode the captured video.
The resolution is set to 1366x768 with framerate at 25 and the command looks like this:
$ ffmpeg -f alsa -ac 2 -i pulse -f x11grab -r 25 -s 1366x768 -i :0.0 \ -vcodec libx264 -pix_fmt yuv420p -preset ultrafast -crf 0 -threads 0 \ -acodec pcm_s16le -y output.mkv
In the command, -i :0.0 means to capture the primary screen (0.0). We're using libx264 video codec. To support some of the media players that does YUV planar color space with 4:2:0 chroma subsampling for H.264 vide, we can use -pix_fmt yuv420p, if no pixel format is specified, yuv444p for H.264 encoding will be used by default.
To stop recording, make the terminal active and then press q.
Here is a summary what we've done:
We captured audio from pulseaudio sound server and encode it to lossless raw PCM with 2 audio channels (stereo). Then, we grab a video stream from X11 at a frame rate of 25 and a size of 1366x768 from the display :0.0 (primary screen) and encode it to lossless h264 using libx264. Using -threads 0 means automatic thread detection. The resulting streams will be muxed in a Matroska container (output.mkv).
Now we need to encode the stream we got.
ffmpeg -i output.mkv -acodec libfdk_aac -ab 128k -ac 2 -vcodec libx264 -preset slow -crf 22 -threads 0 final_video.mp4
We encode the audio to AAC at a bitrate of 128k with 2 audio channels (stereo). We encode the video to the high quality H.264 video compression standard. We use the preset slow and a crf value of 22 for rate control. The output file is final_video.mp4. We can tweak the crf value to get different results. The lower we set the crf value, we get the better quality, and consequently the file size and encoding time will increase, and vice-versa.
If the machine we're using has enough power, we can do it all at once.
ffmpeg -video_size 1366x768 -framerate 25 -f x11grab -i :0.0 -f alsa -ac 2 -i pulse InOneStep.mp4
We may need the pavucontrol to capture application (system) audio instead of microphone.
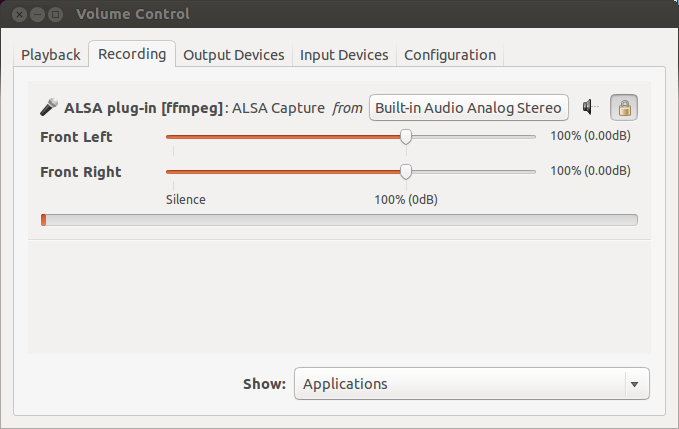
It usually comes with default Ubuntu install. So, we can just fire it up.
$ pavucontrol
To change the input, open up pavucontrol, go to the Recording tab and we'll find ffmpeg listed there. Then, change audio capture from Built-in Audio Analog Stereo to Monitor of Built-in Audio Analog Stereo.
In this chapter, we captured a full screen but we'll extend it to capturing current (active) screen after detecting it by a python code: FFmpeg Screen Recording B - Active Window Screen Capture with Python on Ubuntu B
Ph.D. / Golden Gate Ave, San Francisco / Seoul National Univ / Carnegie Mellon / UC Berkeley / DevOps / Deep Learning / Visualization